Select All of the Following That Describe Metabolic Pathways.
A metabolic pathway is a consecutive process that takes place step after step set of connected biochemical reactions that changes substrate to a product or products through metabolic reactions and intermediate products. Chemistry questions and answers.
Overview Of Metabolism Article Khan Academy
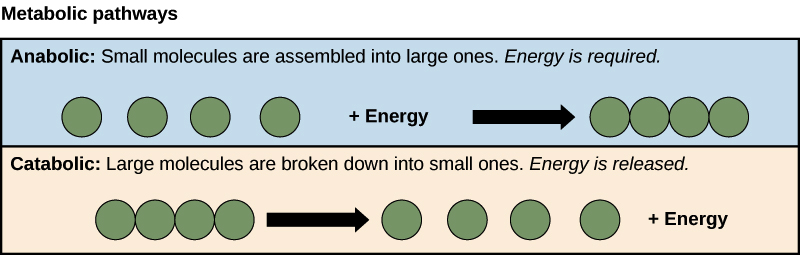
Overview of metabolic pathways energy flow in a cell and anabolism and catabolism.
. Hunger increases and the metabolic rate goes down. Thus the correct answer is option A. Among the given options out of four boxes the first box represents the starting substrate for the pathway and the last box represents the final product.
The metabolic pathway includes a series of reactions. Metabolic Pathway 3. The laws of thermodynamics.
All cells produce substances that are essential for them to function properly. Who are the experts. Identify the locations of the following metabolic pathways.
The three levels at which metabolic pathways are regulated are 1 regulation 2 regulation and 3 regulation. 1the set of molecular reactions in which enzymes make or break down sugars 2chemical reactions that do not involve the use of enzymes and that maintain homeostasis 3a chemical reaction that makes or breaks down molecules 4a linked sequence of chemical. Evaluate the effects of different factors substrate and enzyme availability presence of inhibitors on a given metabolic pathway.
The metabolite flow the rate and direction at which metabolism takes place are called the dynamic state of body constituents. Metabolic Pathway 4. A metabolic pathway refers to a chain of reactions in which the product of the first reaction becomes the substrate for the next reaction and so on.
One of the example is breakdown of the carbohydrates in to glucose molecules. Catabolic pathways produce stable usable cellular energy by synthesizing more complex organic molecules. Genetic cellular biochemical The general term for all types of coordinated sequences of chemical reactions that occur in cells is pathways.
This problem has been solved. First Law of Thermodynamics introduction. Metabolic pathways exist from birth to death of any living organism.
Second Law of Thermodynamics and entropy. Examples of Metabolic Pathways. All metabolic reactions are catalyzed by a set of proteinaceous compounds called enzymes.
Whereas in the plants leaves are the organs with high metabolic activity. Pentose phosphate pathway ONitrogen dissimilation A Entner-Doudoroff pathway O Electron transport system Glycolysis Question 11 The binding of a positive allosteric regulator molecule will. Reaction coupling to create glucose-6-phosphate.
When large molecules are broken down into smaller ones- releases energy exergonic Anabolic reaction. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Hunger decreases and the metabolic rate goes up.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Identify the locations of the following metabolic pathways. Metabolic Pathway 5.
Degradation of organic molecules by anabolic pathways provides the energy to drive catabolic pathways. For example in plants specific metabolic pathways can produce glucose and. In biochemistry a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell.
A series of chemical reactions all involving enzymes and energy beginning with reactants or substrates and ending with products. Question 10 Select all the central metabolic pathways that yield precursor metabolites necessary for life. C coenzymes serve as electron and proton carriers during reactions 4 The first set of reactions or biochemical pathway that occurs during the catabolism of.
And 2 transferring the electrons carried by NADH and FADH2 to the terminal electron acceptor. Anabolic pathways synthesize more complex organic molecules using the energy derived from catabolic pathways. There are two general types of metabolic pathways.
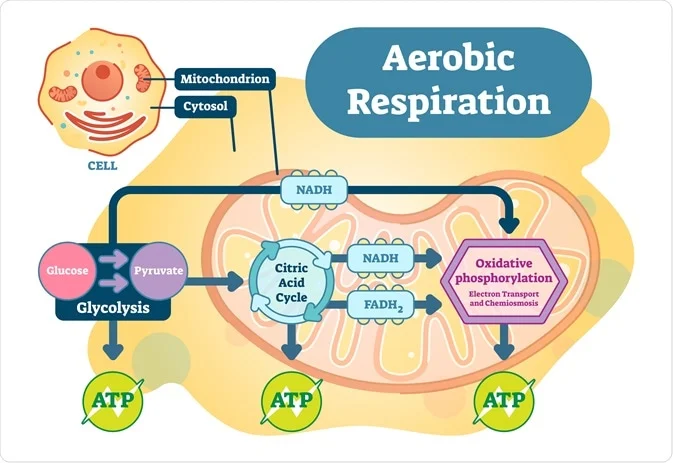
Glucose catabolism encompases two key processes. Which of the following statements best describes a metabolic pathway. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area.
Ii Alternate EMP Pathway-Methyl Glyoxal Pathway. 26 In most cases of a metabolic pathway the product of one enzyme acts as the substrate for the. Cellular respiration is one.
Hence metabolism is an enzyme-catalyzed reaction which provides biomolecules needed by the cells. Both of these responses tend to maintain a. DNA regulates metabolic pathways directly.
10 out of 10 Question 7 How does the body react to rapid weight loss. Describe metabolic pathways as stepwise chemical transformations either requiring or releasing energy and recognize conserved themes in these pathways. 3 Which of the following best describes the role of coenzymes such as NAD during metabolism.
Regardless of their purpose all metabolic pathways share four important features. Metabolic Pathway 1. Glycolysis aerobicanaerobic respiration citric cycleKrebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation are all examples of metabolic pathways that are employed by most all living organisms in some.
The reactants products and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites which are modified by a sequence of chemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes. 1 oxidizing glucose molecules to generate ATP reducing power and precursor metabolites. Metabolic Pathway 2.
Rest two boxes represent the intermediates formed during the. Mevalonic acid pathway 10. Hunger increases and the metabolic rate goes up.
Catabolic pathways release energy while breaking down molecules into simpler molecules. Pentose Phosphate Pathway PPP.

Cell Metabolism Learn Science At Scitable

0 Response to "Select All of the Following That Describe Metabolic Pathways."
Post a Comment